Before we begin explaining , it is important to know what it is that parameters can default to. Because of this, we will first review the difference between arguments and parameters in a function.
In the following code block, we create a function that returns the cube of a given number, defined as y:

The y variable in this example is a parameter—a named variable passed into a function. A parameter must always be contained in a variable and must never have a direct value.
In this case, 10 is an argument—a value passed to a function when it is invoked.
Now lets begin !

Default parameters
Default function parameters allow named parameters to be initialized with default values if no value or undefined is passed.
In the following example, if no value is provided for b when multiply is called, b's value would be undefined when evaluating x * y and multiply would return NaN.

In ES6, you can assign 1 as the default value for y in the function head:
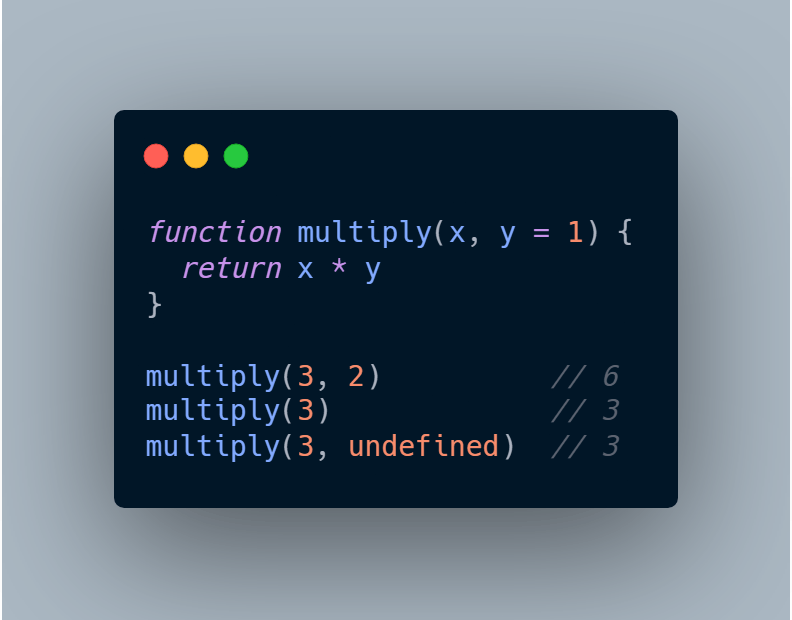
More of JavaScript default parameter
The arguments object
The value of the arguments object inside the function is the number of actual arguments that you pass to the function. For example:
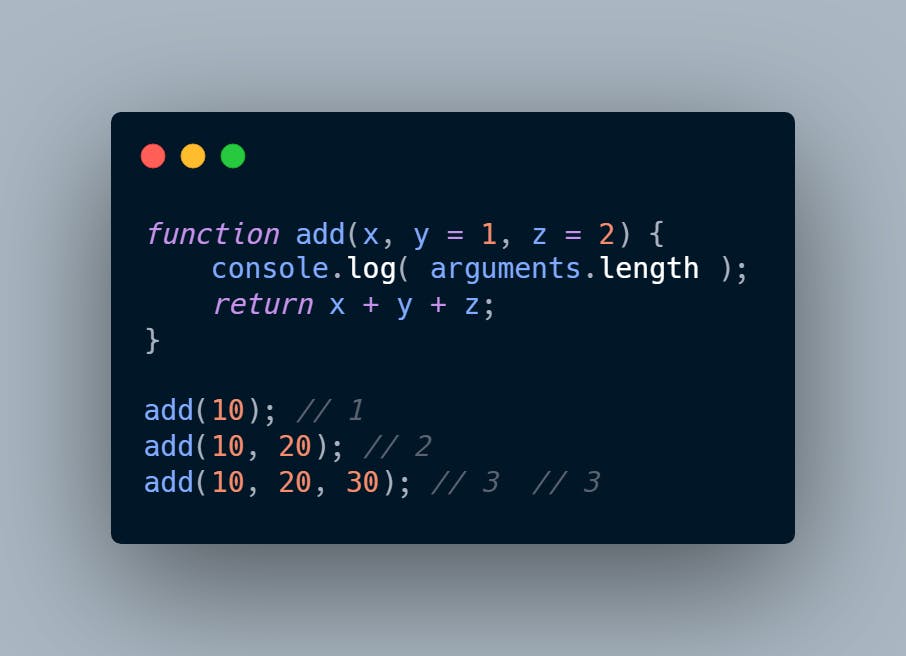
Rest Parameter
The rest parameter syntax allows a function to accept an indefinite number of arguments as an array, providing a way to represent variadic functions in JavaScript.
ES6 provides a new kind of parameter so-called rest parameter that has a prefix of three dots (...). A rest parameter allows you to represent an indefinite number of arguments as an array.
In the code below, arguments are passed more than the parameters, but only the first two arguments will be evaluated. It’s different in the case with rest parameter. With the use of the rest parameter, we can gather any number of arguments into an array and do what we want with them. Javascript code demonstrating addition of numbers using rest parameter.
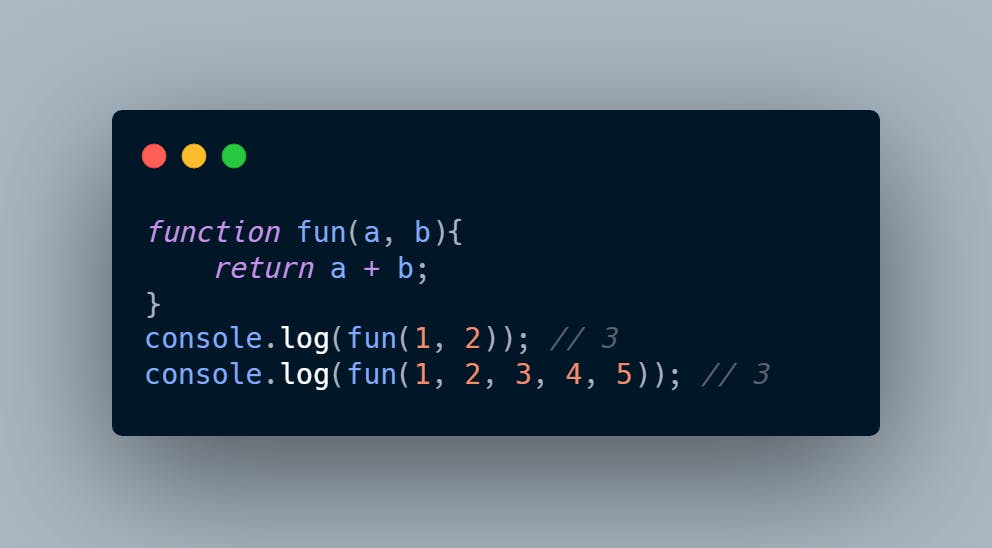
More JavaScript rest parameters examples
JavaScript rest parameters and arrow function
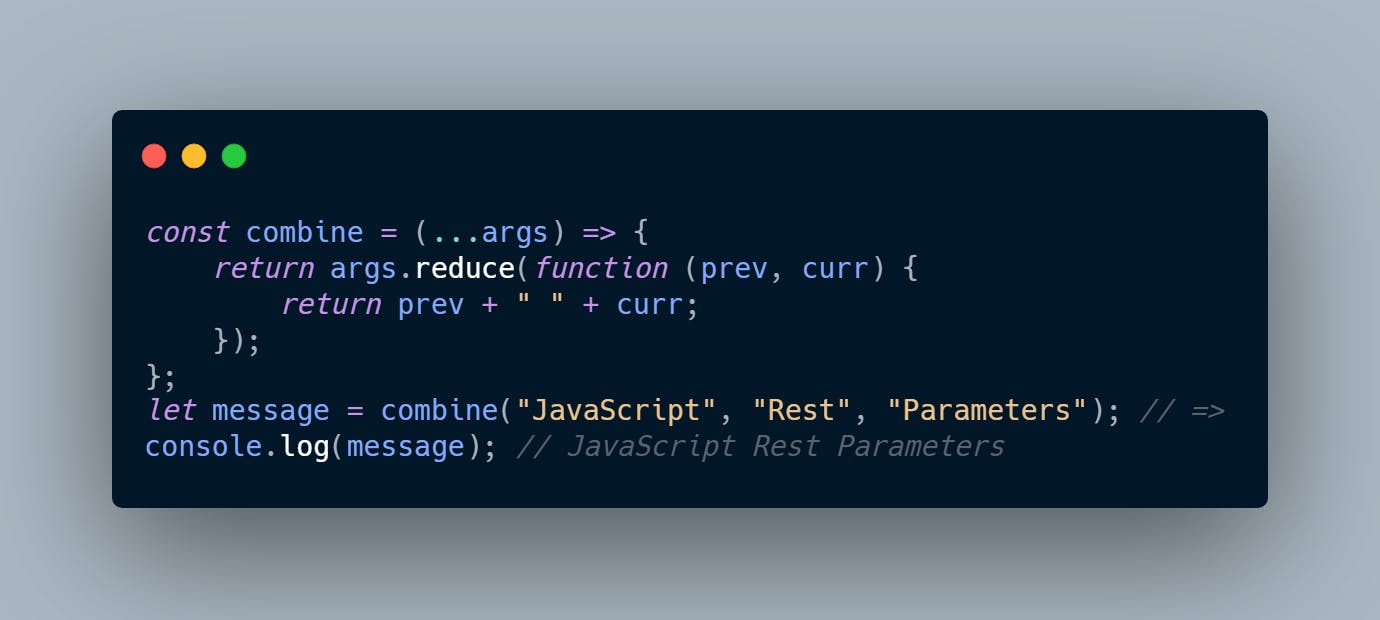
An arrow function does not have the arguments object. Therefore, if you want to pass a number of arguments to the arrow function, you must use the rest parameters. See the following example:
Spread Operator
Spread operator (...) allows an iterable such as an array expression or string to be expanded in places where zero or more arguments (for function calls) or elements (for array literals) are expected, or an object expression to be expanded in places where zero or more key-value pairs (for object literals) are expected.
To use the spread operator in the example below, we insert an element f inside an array, let's have a look:
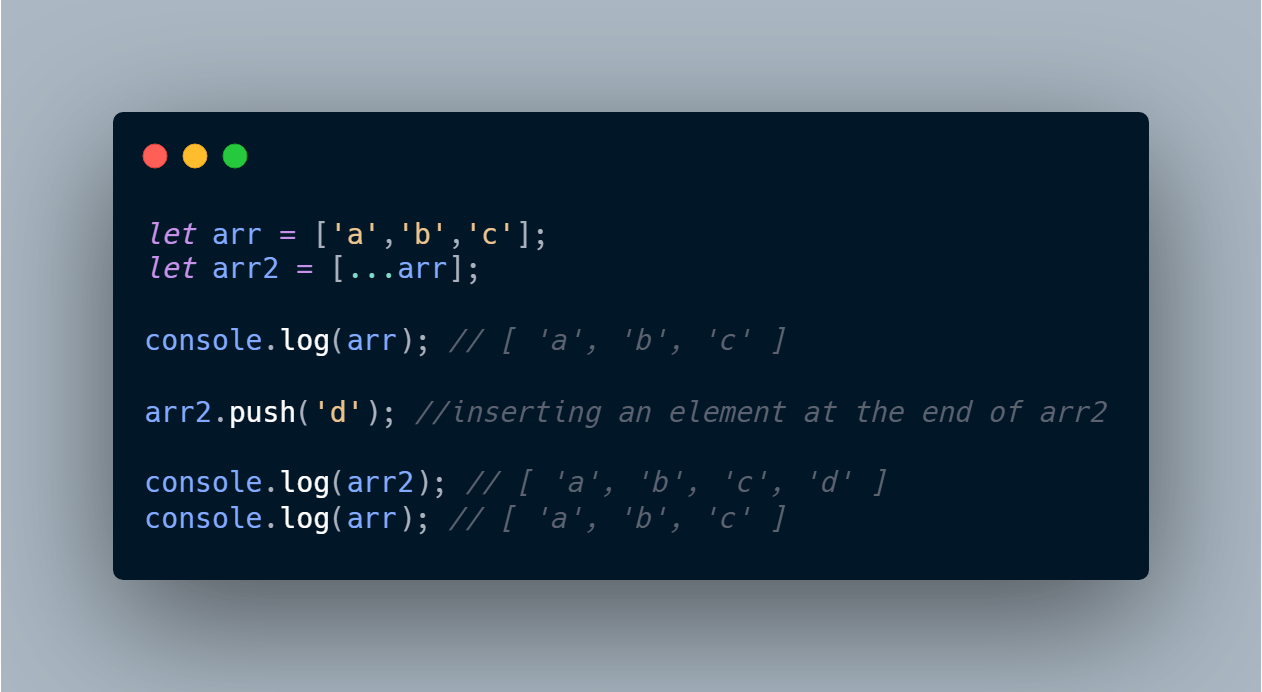
More of Spread operators in JavaScript
JavaScript spread operator and array manipulation
The spread operator allows you to insert another array into the initialized array when you construct an array using the literal form. See the following example:
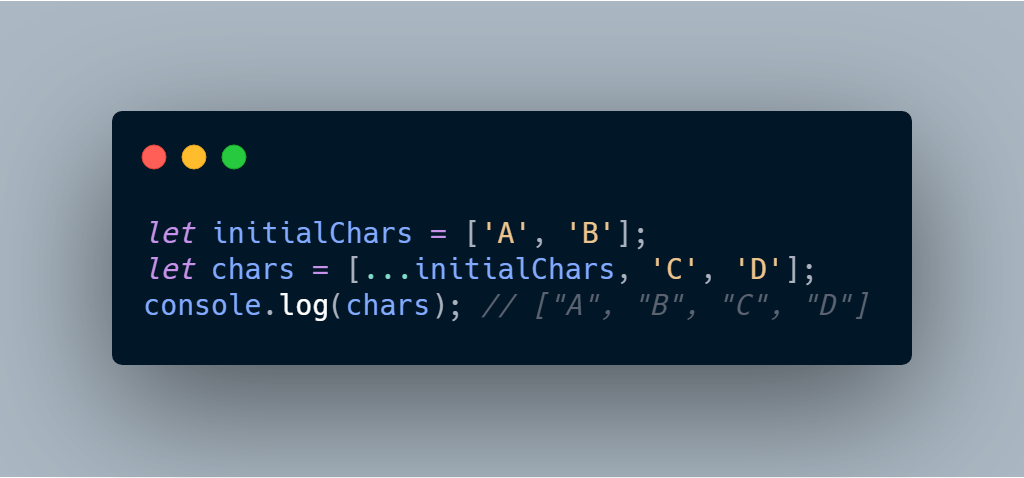
And that mark the end of our topic, I hope you learnt something. Feel free to comment down below.
Stay safe.✌
